Study on the distribution of activity and particle sizes in the nano- and millimetre range in gaseous effluents from nuclear installations with and without filter successfully completed
The study on the distribution of activity and particle sizes in the nano- and millimetre range in gaseous effluents from nuclear installations with and without filter, jointly conducted by BS, Radiochemie München (RCM) and Forschungszentrum Jülich, is completed. The activity distribution as a function of the aerodynamic particle diameter is decisive for the calculation of effective dose to members of the public following the discharge of radioactive substances from nuclear facilities. We investigated this aspect experimentally in the context of changing activities in the course of dismantling of nuclear facilities (no power generation, use of decontamination and segmenting techniques).
We measured the particle mass and activity distribution by particle size during the dismantling phase of two German nuclear power plants.
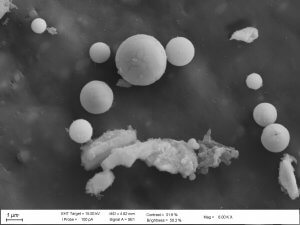
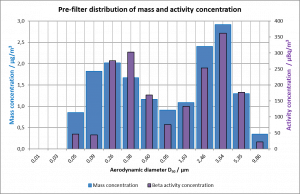
The particle size distribution was investigated at aerodynamic particle diameters between a few nm and more than 10 μm, at the aerosol origin without filtration, in the ambient plant air cleaned by pre-filtering and in the exhaust air emitted from the stacks after passing the stack filtration systems, respectively. This approach allowed evaluation of the filter efficiency by comparing the particle concentrations upstream and downstream of the filtering systems.
The gravimetric measurements yielded bimodal distributions of the particle mass concentration, which approximately coincided with the activity concentration distribution for larger aerodynamic particle diameters. However, the measurement methods reached their limits in determining the activity distribution at aerodynamic diameters below 2.5 μm. The measurements consistently demonstrated the high efficiency of the filter systems.
- Post Categories
- SKS

